Data-driven sales allow you to customize your sales approach to increase your conversion rate. However, attracting leads is only half of the sales process. Since 73% of leads aren’t ready to buy, you still need to nurture them and show them how your products or services will solve their pain points. That’s where data-driven sales can help you by personalizing your interactions with each consumer.
In this article, we will look at key data points to collect about your customers to improve your data-driven sales strategies and create a data-driven sales team.
Key Takeaways:
- Data-driven sales help your company be more competitive by identifying pain points and offering a personalized customer experience.
- Key data metrics include customer information, demographics, and financial status.
- Your data should also include all the customer’s interactions with your business, like previous communications, website visits, and sales.
What Are Data-Driven Sales?
One survey showed that 80 percent of consumers want a personalized shopping experience. Data-driven sales leverage consumer information so your sales team can produce customized content for each customer during the sales process. This personalization improves the customer experience, leading to more sales.
Data-driven sales also help you target each lead and address their pain points to increase the demand for your products or services. For example, a florist who learns a customer was recently engaged can use that data combined with their knowledge of the customer’s budget to offer floral wedding packages.
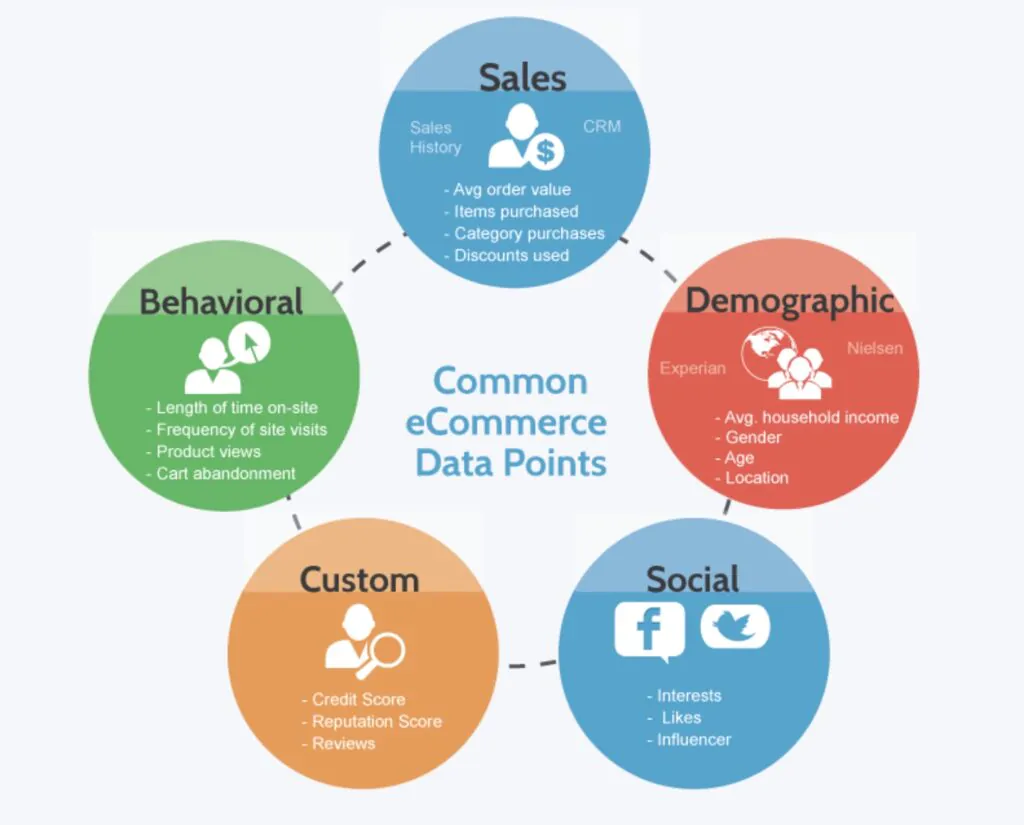
10 Key Customer Data Points That Drive Your Sales
Here are ten crucial data points that will help B2B and B2C businesses create a personalized and targeted sales approach.
Source: RESCI
1. Name and Contact Information
A customer’s name is a unique identifier and should be the first piece of data you collect. You will use this information whenever you send content or deals to the consumer by addressing them by their name at the start of the message. In B2B sales, you may prefer to collect the primary decision maker’s title instead of a specific name, so the correspondences sound personal while remaining formal.
A customer’s contact information includes their email, phone, and address for omnichannel communication during the nurturing process. You can collect a person’s name and contact details through payment forms, newsletter signups, account setup, and inquiry forms.
2. Demographic Information
Your customer’s demographic information will help you create a profile and understand their needs. A greater understanding will also help you qualify leads and alert you to any pain points you can address in your sales pitch.
B2C demographic data points:
- Age
- Location
- Gender
- Marital status
- Educational level
- Job
- Birthdays or anniversaries
B2B demographic data points:
- Company size
- Location
- Age of the company
- Industry
3. Income and Budget
A customer’s income or a business’s budget will give you a better idea of what products or services they can afford. For example, if your sales team only pitched your highest-end products to customers, the customer might grow disinterested in your company and look elsewhere for more reasonable offers.
However, when you know a customer’s budget, you can create offers and send deals that make your products and services more appealing to them. Your sales team will also waste less time pitching products the customer will never buy.
4. Interest and Intent
During your first interactions with a new lead, you should learn their interest and intent. A customer’s interest will let you know if they are undecided and just casually browsing your products to satisfy their curiosity or are actively searching for a solution to a known problem.
Their intent is directly related to their interest. Customer intent can range from searching for product information to looking to purchase immediately.
5. Public Online Data
Everyone leaves a data trail online, which you can follow to add more information to your customer profile than what they provided in forms and through conversations. In addition, an automated system can use your current customer information to search the web for other public data from social media profiles, websites, and online comments.
Online searches can also tell you your customer’s shopping habits to better understand the products that might interest them the most. You can use this data to create personalized online ads or send offers for similar products.
6. Previous Touchpoints
Every time a business or customer interacts with your company, that interaction is a touchpoint. Those touchpoints will tell you a story about your customer, such as how they found out about your company, what channels they prefer to use, and how often they interact with your business. Customers today require more touchpoints than before, averaging between 20 and 500 touchpoints depending on the purchase complexity.
7. Past Interactions
You should save every interaction with customers as those conversations provide valuable insights into their needs. Sales reps can also look back at those conversations when making follow-up calls with customers to avoid repeating the same information. Instead, they can focus on providing new information to create greater value.
Customer interactions include:
- Contact form messages
- Social media comments
- Customer service interactions
- Phone calls
- Email correspondences
- Customer feedback
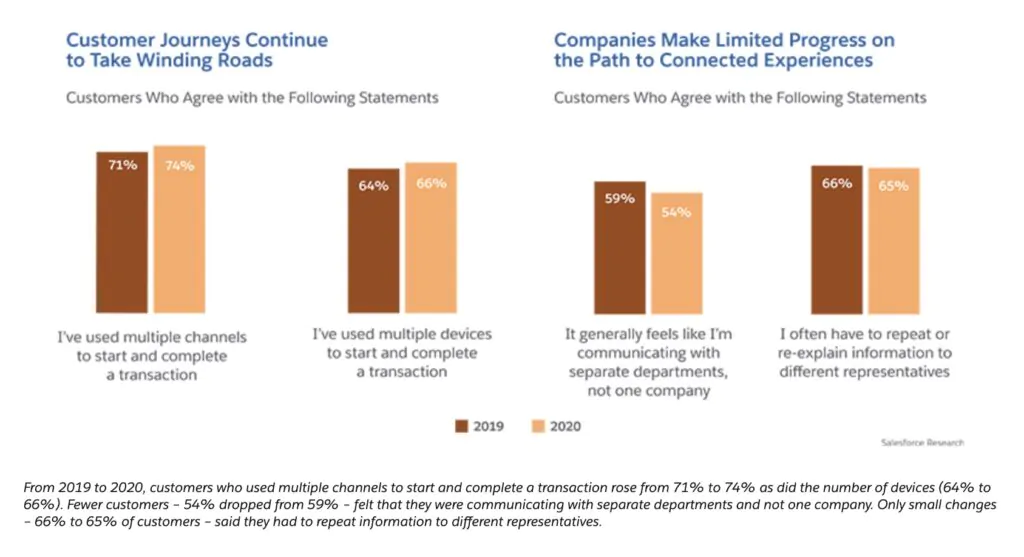
Source: Salesforce
8. Sales History
Tracking a customer’s sales history will let you know if they are a first-time, returning, or loyal customer, influencing your interaction with the consumer. About 64% of consumers don’t mind data-driven businesses saving their purchase history and preferences for personalization purposes. Sales history can refer to products bought, services used, trials signed up for, and booklets downloaded.
9. Location in the Sales Funnel
Your sales team should know a customer’s location in the sales funnel to choose the best sales approach. Is your team’s goal to collect customer data from new customers, or are they selling products to interested consumers?
10. Buyer Persona
Your marketing and sales teams will have target customer personas that outline the types of customers or businesses most likely to purchase from your company. The previous nine data points will help you short your customers by the personas that best fit them, which will give your sales team a strategy for approaching the client.
Track Your Customers With Automation Software
Marketing automation helps you collect and store customer data for an improved data-driven sales approach. Our software will ensure you never lose another lead again as they move through the sales funnel. You can also use the valuable information you collect to offer better, personalized interactions for every customer.
Schedule a demo to see how our automation software can help you track your leads.
Feature Image: istockphoto