A McKinsey survey found that companies that utilize customer analytics extensively see a 115% higher ROI and 93% higher profits than their peers. This is because leveraging customer data analytics allows these companies to sell more effectively. With richer sales data at their fingertips, their salespeople understand their target audience better, nurture leads more effectively, and close deals at the right time.
Today, data forms a central part of smart decision-making in all organizations. It is the key to unlocking your Marketing and Sales departments’ full potential by aligning them into a seamless, harmonious system.
But what is customer analytics? And how do you make it work for your organization?
Key Takeaways:
- Customer data analytics comes in various flavors. It aims to use data to answer questions on a business’s past, present, and future.
- Extensive usage of customer data analytics directly correlates with increased sales and higher profits and ROI.
- Tools such as CRM, SEP, and CDP help in forming a 360-degree view of each customer.
What Is Customer Data Analytics?
In most cases, the target audience you are trying to attract resembles your present customer base. You are looking for more people with similar needs, wants, interests, preferences, values, and behavior as your current customers, and you’re trying to get them into your funnel – online or in-store.
This is why you need customer data analytics.
In essence, customer data analytics is the systematic collection, organization, storage, and analysis of your present customers’ data to understand their pain points, price sensitivity, and other factors that influence their purchase decision-making process.
You can use this customer information and behavior database to attract, convert, and retain your ideal customers.
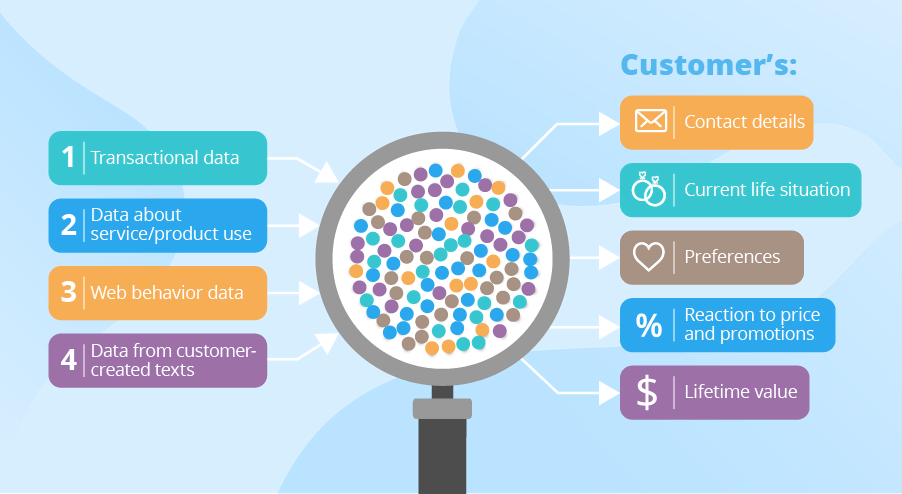
Source: OmniSci
Types of Customer Data Analytics
Depending on the type of insights you want to derive from your data, customer analytics is divided into four types:
Descriptive Customer Analytics
This is the most basic type of customer analytics. It involves studying and analyzing raw data about past events from various data streams to understand why an event or change occurred.
For example, you might look into the open rate of emails sent to all leads to investigate a drop in sales in the last quarter.
Descriptive analytics asks the question, “What happened?” It is helpful for understanding past events with the aim of preventing the undesirable ones from reoccurring and replicating the desirable ones.
Diagnostic Customer Analytics
If your business is facing significant issues in customer acquisition, satisfaction, or retention, you obviously need to solve them as soon as possible. Diagnostic customer analytics asks the question, “Why did this happen?”
To answer this, you analyze your present and past customer data using techniques like data discovery, data mining, etc., in an attempt to diagnose the root cause of the problems you’re facing.
For example, if leads are dropping out of your funnel after testing out your product, you know that one feature or the other isn’t probably working as expected.
Predictive Customer Analytics
Data isn’t just about learning from the past and fixing the mistakes of the present. It can provide you with some excellent estimates for the future too.
Predictive analytics involves analyzing data by identifying patterns, trends, and forecasting key business metrics based on these trends with the help of algorithms and models. While these forecasts might not always be completely accurate, they do give you a practical insight into the future and answer the question, “What is likely to happen?”
One example of predictive customer analytics would be looking at how customers use your product and feeding the results into your lead-to-revenue (L2R) and demand generation models.
Prescriptive Customer Analytics
Prescriptive customer analytics is just an extension of predictive customer analytics.
Suppose predictive customer analytics gives you a range of numbers you can expect to achieve in the future. In that case, prescriptive customer analytics tells you how to leverage these insights to take the best possible course of action.
An example of using prescriptive customer analytics would be coming up with a 15% discount offer on a product to meet sales goals, considering reduced demand.
Why Customer Data Analytics Matters
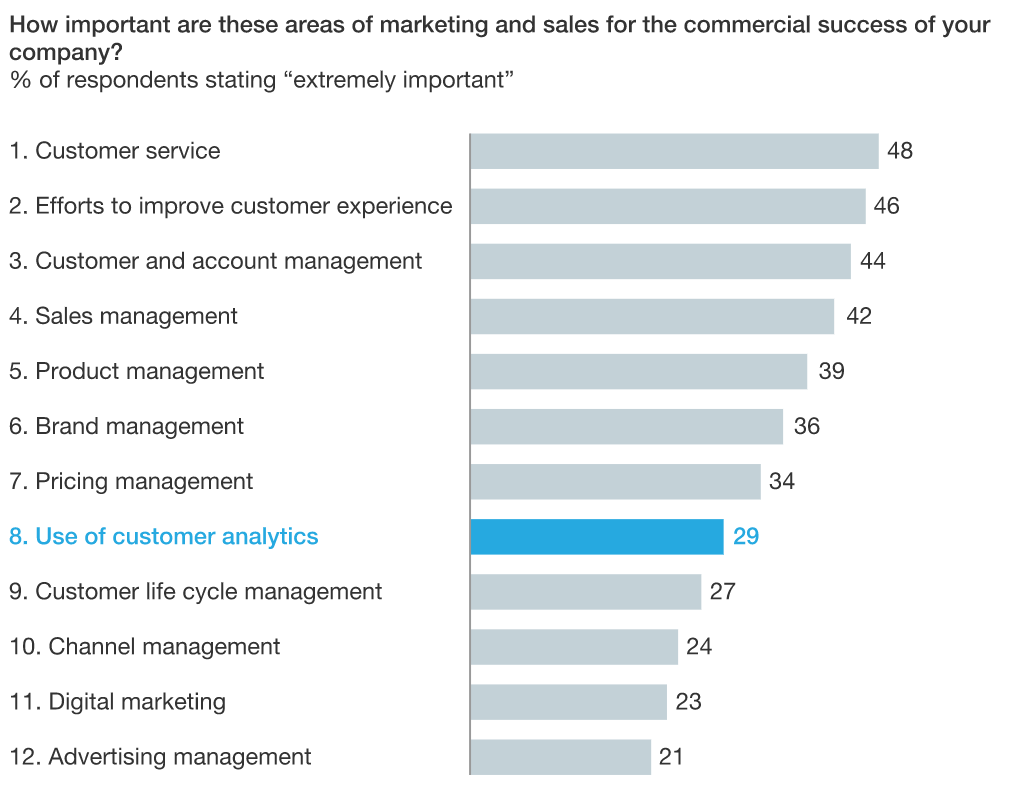
The McKinsey survey found that customer analytics lags behind other areas in perceived importance for driving sales.
Source: McKinsey & Company
And yet, organizations that made extensive use of customer data analytics outperformed their competitors and peers by 82% in sales and 112% in sales growth.
Clearly, companies are continuing to underestimate the importance of customer data analytics. Customer analytics gives you insights into your ideal customer’s behavioral patterns and psychology, using which you can build a fact-based decision-making process for all sales and marketing initiatives.
Another primary reason customer data analytics is essential for your company is because it aids in the creation of a single customer view (SCV). Building SCVs of your customers helps you pinpoint the highs and lows of your sales process and gives your reps critical insights for nurturing qualified leads, personalizing and customizing deals for clients, and retaining existing customers.
How to Collect and Store Customer Data
Now that you know how important it is to analyze customer data, the question arises… How do you gather and store customer data effectively to be accessed and used by your sales and marketing teams on-demand?
Here are some pointers:
1. Plan Your Data Collection Channels
Before you start collecting customer data, you need to decide the type of data you want to collect. Only then will you know the sources, media, and channels where you can hunt for it.
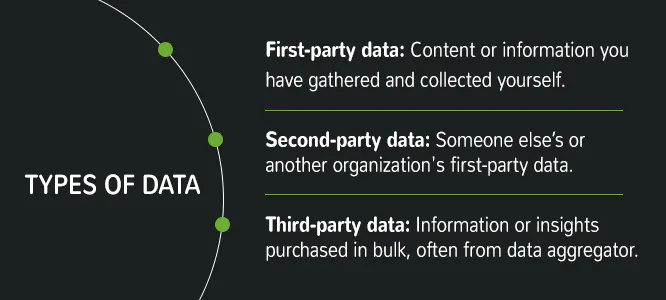
Data is of three types: first-party data, second-party data, and third-party data.
Source: Lotame
Based on the audience segment you choose to target, always keep a check on your jurisdiction’s data protection and privacy laws. This will help you avoid a lot of legal and PR trouble later.
It’s essential to list out the exact information you want to collect – from your audience, leads, and customers. This could be something as simple as their gender and age (demographic information) or something as complex as the CRM used by the company they work for (technographic information).
Lastly, ensure that your sales team has the right tools to gather, export, mine, visualize, organize, and present data. Some of the best tools for collecting customer data include Google Analytics and Hotjar.
2. Streamline Your Data Collection Process with a CDP
A couple of fundamental tools you’ll need to streamline your data collection process is a Customer Data Platform (CDP).
A Customer Data Platform helps you integrate the different types of data together. Its biggest advantage is that you can use it to form a unified customer view (SCV) of your leads and customers. It allows you to sort your data in various ways and form a customer view that works for you.
Your CDP can also connect with other software and tools in your martech stack to allow the seamless flow of data through various stages of your sales funnel.
3. Store Your Data Strategically
Data storage is a crucial step in the data collection process that is underestimated by several businesses.
Storing data is more than adding it to a database – your data must be organized and accessible so that it is readily available to your sales reps as and when needed.
This ensures that a consistent, uniform brand tone and strategy is delivered across all franchises and dealerships for multi-location businesses.
To achieve this, you can add your CRM or sales engagement platform (SEP) to your martech stack. These tools can readily connect with your CDP and help you store your data strategically.
Data warehouses are also a good option for large businesses with multiple physical outlets that’d like to store all of their data in one place.
4. Analyze Your Data
Once your data has been collected, vetted, streamlined, and stored strategically, the only step that remains is to analyze it. This step forms the crux of customer data analytics.
There are many customer analytics tools available in the market – choose one or more that are right for you and make sure your sales reps aren’t wasting half a day in examining and formatting the information available to them.
Better Understanding, Better Experience
In an increasingly competitive market scenario, a crystal clear understanding of who your ideal customer is and how to sell them your product is an invaluable skill for your sales reps.
If you’re looking for a customer data analytics solution, you have one primary goal: democratize data and make it accessible to different departments at the right times. This helps in aligning your Marketing and Sales and creating a consistent, seamless experience for customers – a significant challenge for businesses that operate chain stores, dealerships, or franchises in multiple geographic regions.
Do you run a multi-location business with critical knowledge gaps along your customer journey? Are you struggling to find out what your customers need? Schedule a call with us to dig deeper into customer data and use the insights to drive more sales and revenue.
Featured image: Pexels